Running an online business requires a seamless and secure payment process. Understanding the difference between payment gateways and merchant accounts is crucial for accepting online payments effectively. This guide will demystify these two essential components, providing a clear understanding of how they work together to facilitate online transactions. Choosing the right payment gateway and merchant account can significantly impact your business’s bottom line, affecting transaction fees, processing times, and overall customer experience. We will explore the key features and benefits of each, enabling you to make informed decisions for your online business.
This simple guide will break down the complexities of payment gateways and merchant accounts, highlighting their individual roles in the payment process. We’ll explore the various types of payment gateways available, such as hosted, self-hosted, and API-hosted, and delve into the different types of merchant accounts, including dedicated and aggregated. By understanding the nuances of these systems, you’ll be empowered to optimize your online payment processing, improve conversion rates, and ultimately grow your online business. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to refine your existing payment infrastructure, this guide provides valuable insights to help you navigate the world of online payment processing.
What is a Payment Gateway?
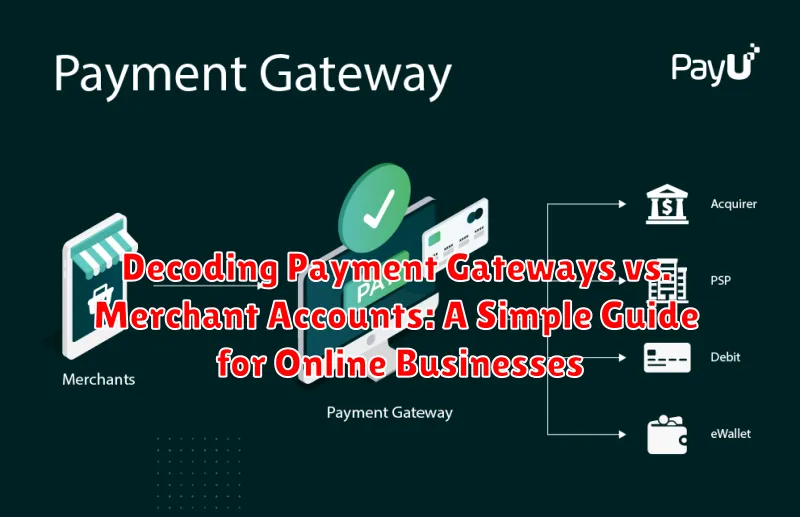
A payment gateway is the technology that securely authorizes online credit and debit card payments for e-businesses, online retailers, bricks and clicks, or traditional brick and mortar. It acts as a bridge, connecting your customer, your business, and the payment processor.
Think of it like this: when a customer enters their payment information on your website’s checkout page, the payment gateway encrypts that sensitive data and transmits it securely to the payment processor. It then receives authorization from the payment processor and relays that information back to your website, allowing the transaction to be completed. Essentially, a payment gateway facilitates the transfer of payment information between the various parties involved in a transaction.
Payment gateways are essential for accepting online payments and ensure secure transactions, protecting both businesses and customers from fraud. They are responsible for authorizing the payment and ensuring the funds are transferred safely from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account.
How Payment Gateways Work
A payment gateway acts as a bridge between your online store and the payment processor. Think of it like a digital point-of-sale system. When a customer makes a purchase, the payment gateway securely captures their credit card information.
This information is then encrypted and transmitted to the payment processor for authorization. The payment processor communicates with the customer’s bank to verify the funds. Once approved, the payment gateway relays the approval back to your online store, allowing the transaction to be completed.
This entire process happens within seconds, providing a seamless checkout experience for the customer. Security is paramount, and payment gateways employ robust encryption methods to protect sensitive data throughout the transaction.
What is a Merchant Account?
A merchant account is a special type of bank account that allows businesses to accept payments via credit and debit cards. Think of it as a holding area for customer funds before they are transferred to your business bank account. It’s a critical component for any business looking to process card transactions online or in person.
Essentially, it acts as an agreement between your business, a merchant acquiring bank (also known as an acquirer), and payment card networks (like Visa, Mastercard, or American Express) that authorizes you to accept card payments. The acquiring bank assumes the risk associated with processing these transactions, as customers may dispute charges or initiate chargebacks. Therefore, obtaining a merchant account involves an application process where the bank assesses your business’s creditworthiness and risk profile.
How Merchant Accounts Work
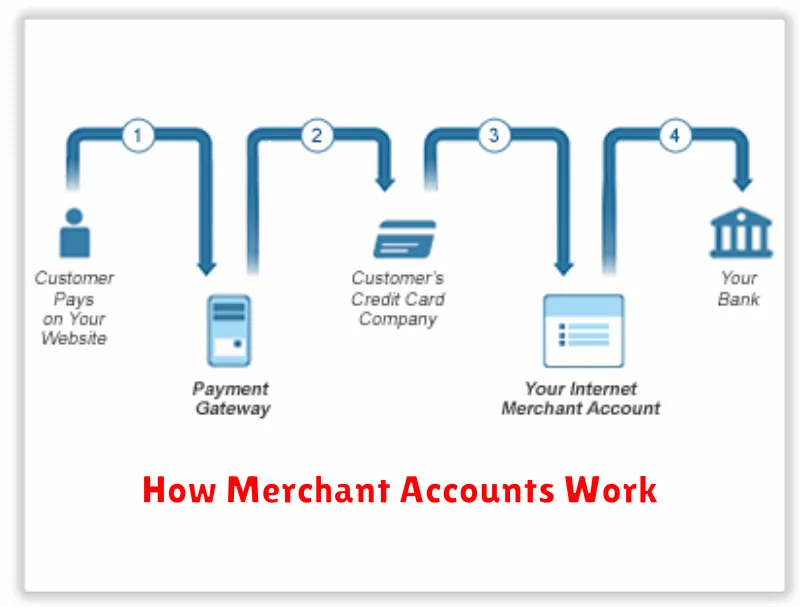
A merchant account acts as a dedicated holding area for customer payments before they are transferred to your business bank account. Think of it like a temporary escrow account specifically for processing credit and debit card transactions.
When a customer makes a purchase, the funds are first authorized by the customer’s issuing bank. The payment gateway then transmits this authorization to your merchant account. The acquiring bank (the bank that provides your merchant account) then deposits the funds into your merchant account, minus any processing fees.
From there, the funds are typically settled (transferred) to your business bank account on a regular schedule, often daily or weekly, based on your agreement with the acquiring bank. This process involves batch processing where transactions are grouped together for settlement. The time it takes for funds to appear in your business bank account can vary depending on factors such as processing times and weekends.
Key Differences Between Payment Gateways and Merchant Accounts
While payment gateways and merchant accounts work together, they are distinct entities. A payment gateway is the online equivalent of a physical point-of-sale terminal. It authorizes transactions and securely transmits data. A merchant account, on the other hand, is a dedicated bank account where funds from processed transactions are deposited.
Think of it this way: the payment gateway is the messenger, and the merchant account is the destination. The gateway facilitates the movement of funds, while the merchant account receives and holds them before they are transferred to your business bank account.
| Feature | Payment Gateway | Merchant Account |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Processes transactions | Receives funds |
| Analogy | POS terminal | Business bank account |
| Necessity | Required for online payments | Required for accepting card payments |
Choosing the Right Payment Gateway and Merchant Account for Your Business
Selecting the right payment gateway and merchant account is crucial for a smooth and secure checkout experience. Several factors should influence your decision. Consider your business size and sales volume. High-volume businesses may benefit from negotiated rates with dedicated support. Transaction fees vary between providers, impacting your bottom line. Evaluate the types of payments you accept – credit cards, debit cards, or alternative payment methods.
Security features are paramount. Look for providers offering fraud protection and data encryption. Integration with your existing e-commerce platform simplifies setup and streamlines operations. Finally, consider the level of customer support offered by each provider. Prompt and reliable assistance can be invaluable when issues arise.
Benefits of Using Both a Payment Gateway and Merchant Account
Leveraging both a payment gateway and a merchant account offers several key advantages for online businesses. This combined approach provides a more streamlined and secure payment processing experience.
A merchant account grants you direct control over your funds. Payments are deposited directly into your account, giving you quicker access to your revenue. This also offers greater transparency into transaction details and fees.
Payment gateways enhance security by encrypting sensitive customer data during transactions. This protects both your business and your customers from fraud. They also offer flexibility by supporting various payment methods, allowing you to cater to a wider customer base. Accepting diverse payment options, from major credit cards to digital wallets, can significantly improve conversion rates.
Together, a merchant account and payment gateway create a robust and scalable solution. This allows your business to handle a larger volume of transactions efficiently as it grows. This scalability is crucial for long-term success in the competitive e-commerce landscape.
Common Fees Associated with Payment Gateways and Merchant Accounts

Understanding the fee structures of both payment gateways and merchant accounts is crucial for managing your business’s finances. While they work together, they often have separate fee schedules.
Payment gateway fees typically include:
- Transaction fees: A percentage or flat fee charged per transaction processed.
- Monthly fees: A recurring charge for using the gateway’s services.
- Setup fees: A one-time charge for setting up your account.
- Chargeback fees: A fee charged when a customer disputes a charge and wins.
Merchant account fees often consist of:
- Interchange fees: Paid to the card-issuing bank.
- Assessment fees: Paid to the card network (e.g., Visa, Mastercard).
- Monthly fees: A recurring charge for maintaining the account.
- Early termination fees: A fee for closing the account before the contract ends.
Be sure to compare pricing models and fee structures from different providers to find the most cost-effective solution for your business.
Integrating Payment Gateways and Merchant Accounts with Your Online Store
Integrating payment processing into your online store is crucial for accepting payments and facilitating transactions. The integration process typically involves connecting your chosen payment gateway and merchant account with your e-commerce platform.
Most popular e-commerce platforms offer seamless integrations with various payment gateways. This often involves installing a plugin or extension specifically designed for your chosen gateway. Configuration typically requires entering your merchant account details and API keys provided by the payment gateway.
Testing the integration is a vital step before going live. This ensures that transactions are processed correctly and securely. Test transactions allow you to verify that funds are transferred to your merchant account and that customer data is handled appropriately.
Some platforms offer hosted payment solutions. With this approach, customers are redirected to a secure payment page hosted by the payment gateway, simplifying the integration process and reducing PCI DSS compliance requirements for your online store.